Troubleshooting connectivity with Network Watcher
Blocked traffic in Azure? Learn to diagnose connectivity issues fast with Network Watcher. Trace packets, check rules, and fix connectivity.

The Goal
Discover why virtual machinevm-appcannot connect to virtual machinevm-dbon port 3306 (MySQL) in our lab environment setup.
The Lab
This lab is also available on YouTube
We’ll use the following setup:
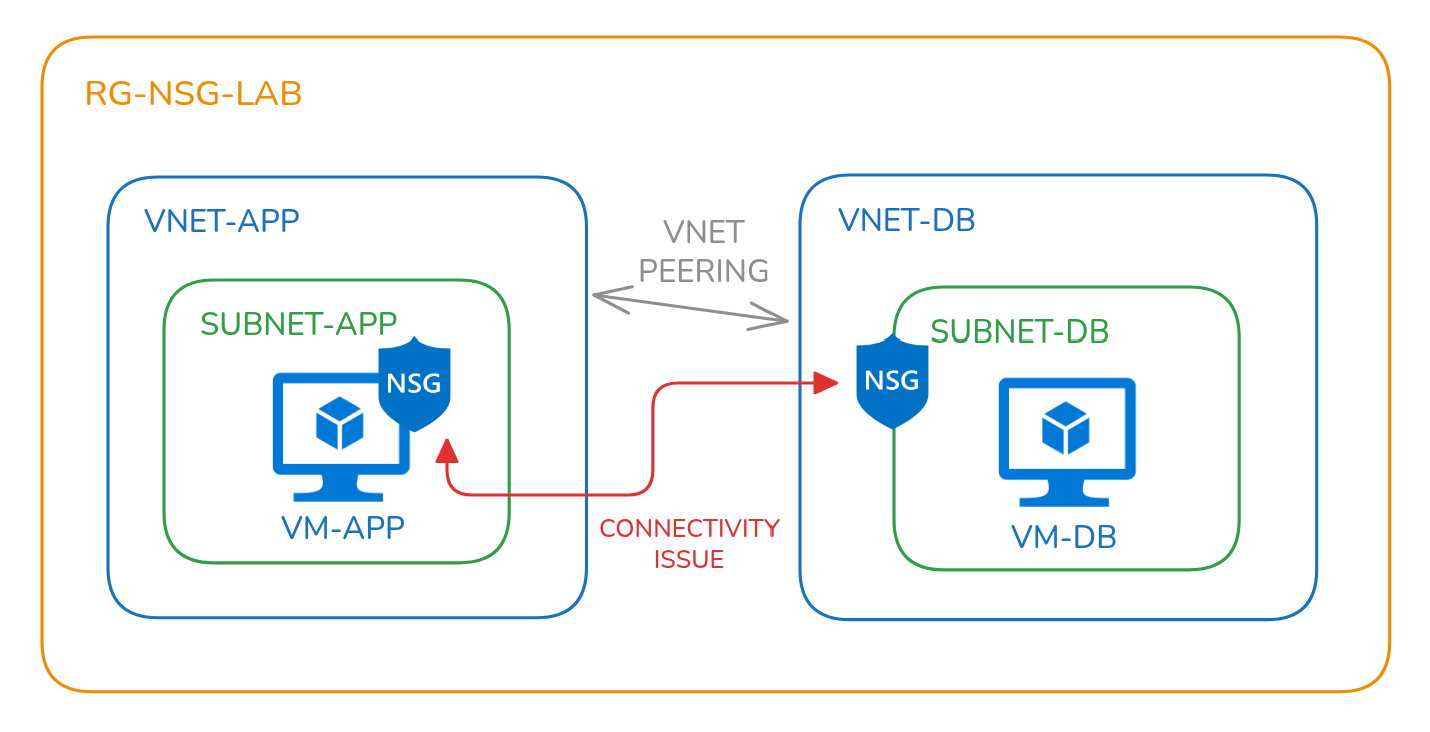
| Component | Name | Notes/ |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Group | rg-nsg-lab | Central container for all resources |
| Virtual Networks | vnet-appvnet-db | Each VNet contains one subnet |
| Subnets | subnet-appsubnet-db | Used to host VMs |
| Virtual Machines | vm-app(*Apache installation) vm-db (+MySQL installation) | Each VM resides in its respective subnet |
| Network Security Groups (NSGs) | nsg-app on vm-app NIC nsg-db on subnet-db | Misconfigured on purpose Deny rule for VNetOutboundMisconfigured on purpose Deny rule for VNetInbound |
| VNet Peering | One wayvnet-dbto vnet-app | Misconfigured on purpose |
*Use the following commands to install Apache web server on vm-app
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y apache2 && echo -e "Listen 0.0.0.0:80\nListen [::]:80" | sudo tee /etc/apache2/ports.conf > /dev/null && sudo systemctl restart apache2
+Use the following commands to install MySQL database server on vm-db
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y mysql-server && sudo sed -i "s/^bind-address.*/bind-address = 0.0.0.0/" /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf && sudo systemctl restart mysql
The Why
NSGs are often the first place to look when traffic between Azure resources isn’t flowing. But with rules applied at both subnet and NIC levels, it’s easy to miss something. Azure Network Watcher provides tools to simulate traffic, inspect effective rules, and pinpoint the exact rule causing a block.
Troubleshooting using Network Watcher
Network Watcher automatically creates a resource group named NetworkWatcherRG that holds any resources used by Network Watcher tools:
- IP Flow Verify Checks if NSG rules allow or deny specific traffic between a source and destination IP, port, and protocol. Useful for pinpointing NSG rule conflicts.
- NSG Diagnostics Provides insights into NSG configuration, including rule conflicts, priority issues, and traffic flow analysis. Helps validate NSG setup across NICs and subnets.
- Next Hop Determines the next hop for a packet from a VM to a destination IP. Useful for verifying routing paths and peering configurations.
- Effective Security Rules Displays the cumulative NSG rules applied to a VM’s NIC or subnet. Helps understand which rules are actually enforced on the VM.
- Connection Troubleshoot Simulates traffic between endpoints to test connectivity. Evaluates routing, NSGs, and listener availability, making it ideal for end-to-end diagnostics.
We’ll use these tools to troubleshoot the misconfigurations created in this lab.
Test 1 - IP Flow Verify
To test TCP connectivity from vm-app to vm-db on port 3306 using source port 54321 (just a random high-numbered port like a real app might use). The test failed due to a deny rule for VNetOutbound in nsg-app.
- Source VM:
vm-app - Destination IP:
10.2.0.4(IP ofvm-db) - Destination Port:
3306(MySQL) - Source Port:
54321(just a random high-numbered port like a real app might use) - Result: Access Denied
- Reason: Deny rule for
VNetOutboundinnsg-appblocked the traffic
To test TCP connectivity from vm-db to vm-app on port 80 using source port 54321 (just a random high-numbered port like a real app might use). The test failed due to the default deny rule in nsg-db.
- Source VM:
vm-db - Destination IP:
10.1.0.4(IP ofvm-app) - Destination Port:
80(HTTP) - Source Port:
54321(just a random high-numbered port like a real app might use) - Result: Access Denied
- Reason: Default deny rule in
nsg-dbblocked the traffic
Test 2 - NSG Diagnostics
To analyse traffic flow from vm-app to vm-db on port 3306. The test confirmed that the traffic was denied due to a rule applied on the NIC of vm-app.
- Target VM:
vm-app - Protocol: TCP
- Direction: Outbound
- Source Type: IPv4 address/CIDR
- IPv4 address/CIDR: 10.1.0.4 (IP of
vm-app) - Destination IP:
10.2.0.4(IP ofvm-db) - Destination Port:
3306(MySQL) - Result: Access Denied
- Reason: NSG rule on
vm-appNIC blocked outbound traffic tovm-db
This test evaluated outbound traffic from vm-db to vm-app on port 80. The traffic was denied due to an NSG rule applied at the subnet level.
- Target VM:
vm-db - Protocol: TCP
- Direction: Outbound
- Source Type: IPv4 address/CIDR
- Source IP:
10.2.0.4(IP ofvm-db) - Destination IP:
10.1.0.4(IP ofvm-app) - Destination Port:
80(HTTP) - Result: Access Denied
- Reason: NSG rule on
subnet-dbblocked outbound traffic tovm-app
Test 3 – Next Hop
This test tells us where a network packet will next be routed from source in process to get to its destination.
vm-app to vm-db
- VM:
vm-app - Source IP:
10.1.0.4(IP ofvm-app) - Destination IP:
10.2.0.4(IP ofvm-db) - Result: Next hop is VirtualNetworkPeering, which gives us a clue that we should check VNet peering settings.
vm-db to vm-app
- VM:
vm-db - Source IP:
10.2.0.4(IP ofvm-db) - Destination IP:
10.1.0.4(IP ofvm-app) - Result: Next hop is VirtualNetworkPeering, which gives us a clue that we should check VNet peering settings.
Test 4 – Effective Security Rules
This test examined the effective NSG rules applied to each VM to understand how traffic is being filtered at both the NIC and subnet levels.
vm-app
- NSG Location: Applied directly to the NIC.
- Effective Rules: Reflect only the NSG associated with the NIC.
- Implication: Traffic filtering is controlled at the NIC level.
vm-db
- NSG Location: Applied to
db-subnet - Effective Rules: Reflect NSG rules inherited from the subnet.
- Implication: All VMs within the subnet share the same NSG rules.
Test 5 - Connection Troubleshoot Tool
This test simulates full connectivity diagnostics between two virtual machines. It effectively generates a report of the previous tests we ran. The following settings were used:
vm-app to vm-db
- Source Type: Virtual machine
- Source VM:
vm-app - Destination Type: Virtual machine
- Destination VM:
vm-db - Preferred IP Version: IPv4
- Protocol: TCP
- Destination Port:
3306 - Source Port:
54321(just a random high-numbered port like a real app might use) - Diagnostic Tests: Connectivity, NSG diagnostic, Next hop, Port scanner
vm-db to vm-app
- Source Type: Virtual machine
- Source VM:
vm-db - Destination Type: Virtual machine
- Destination VM:
vm-app - Preferred IP Version: IPv4
- Protocol: TCP
- Destination Port:
80 - Source Port:
54321(just a random high-numbered port like a real app might use) - Diagnostic Tests: Connectivity, NSG diagnostic, Next hop, Port scanner
The Conclusion
Azure Network Watcher makes connectivity troubleshooting far more precise. Instead of guessing which rule is the culprit, you get a clear answer fast. Whether you're debugging a blocked port or validating your security posture, these tools are essential for any Azure engineer.
Using a VPN is a secure and simple way to protect your data.
If you'd like to support my work, show your appreciation!


Comments ()